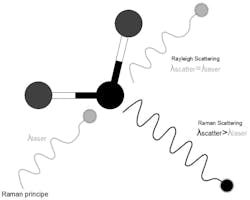
Raman spectroscopy, a transformative analytical technique, has revolutionized our exploration of molecular composition and structure across diverse materials. Through the inelastic scattering of light by chemical bonds, it offers unique insights into vibrational energy and distinct chemical signatures. Recent technological strides have rendered Raman instruments more stable and affordable, expanding their applications from life sciences to materials science.
Modern Raman instruments, utilizing continuous-wave or pulsed lasers, span the UV to near-infrared spectrum. Equipped with sensitive CCD detectors, advanced devices suppress background Rayleigh scattering and combat fluorescence through confocal apertures and wavelength shifting. Cooling systems for Raman CCDs have evolved into simpler thermoelectrically cooled detectors. High-end instruments now feature multiple lasers, software-selected and calibrated with minimal user intervention, reducing background fluorescence.
The Crucial Role of Lasers
In Raman spectroscopy, laser choice is pivotal. A 532 nm green laser, commonly used for its cost-effective sensitivity, can be replaced with a 488 nm blue laser for experiments requiring higher sensitivity. However, the wavelength of the laser influences sample fluorescence; a 785 nm infrared laser is often preferable when fluorescence is an issue, offering versatility at the expense of some sensitivity. Longer-wavelength lasers, such as 633 nm, strike a balance between avoiding fluorescence and mitigating sample heating.
Cutting-edge Raman Approaches
Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS), an extension of Raman spectroscopy, finds applications in ultrasensitive sensing, including DNA and virus analysis. Amplifying Raman signals through electromagnetic and chemical mechanisms on nanostructured metal surfaces, SERS achieves signal enhancements on the order of 10^10 to 10^11, crucial for overcoming the inherent weakness of normal Raman scattering.
Raman spectroscopy seamlessly integrates with microscopy, particularly confocal microscopy, using laser-based Raman microscopes. This integration is invaluable for analyzing tiny structures, enhancing spatial resolution for 3D imaging.
Raman spectroscopy’s significant contributions to biomedical imaging enable noninvasive, in vitro visualization of biological structures. Combined with confocal microscopy, it provides high-resolution images, aiding disease diagnosis and identifying medicines’ compositions in the life sciences.
Increasingly employed in clinical disease detection, Raman spectroscopy distinguishes between healthy and malignant tissues based on distinct spectra. Eliminating the need for biopsies and lab analysis, it offers faster and more efficient results, playing a critical role in detecting various cancers.
NIR Raman Spectroscopy
Near-infrared (NIR) Raman spectroscopy, a noninvasive approach for brain analysis, measures neurotransmitter concentrations through thin skull regions with high precision. Advanced techniques, such as surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, amplify signals, enhancing accuracy in neuroscience applications.
Raman spectroscopy serves as a versatile, nondestructive identification tool across various industries, requiring careful selection of components to minimize noise and meet specific application requirements.
Applications of Raman Spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy finds applications in scientific research, pharmaceutical monitoring, non-destructive identification of substances, analysis of historic artworks, identification of polymorphism, tracking changes in processes, explosive detection, strain measurements, and temperature sensing.
Raman spectroscopy’s remarkable ability to reveal molecular characteristics, coupled with technological advancements, has propelled it into diverse applications, particularly in life sciences and medical diagnostics. This potent analytical tool continues to evolve, promising further breakthroughs in understanding and analyzing the world around us.
Do not hesitate to contact Shanghai Optics today. We’d be more than happy to discuss your projects and how best they can become a success.